How Long Does My Skin Leak After Cellulitis
Cellulitis
51263 34 Information forImages of Cellulitis



Overview
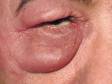
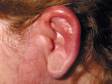
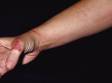
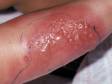
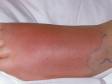
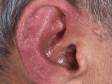
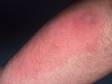
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and is most often caused by the leaner Streptococcus or Staphylococcus. These bacteria are able to enter the skin through small-scale cracks (fissures), causing the sudden advent of redness, swelling, and warmth in the peel. Cellulitis is sometimes accompanied by fever, chills, and full general fatigue.
If the infection is left untreated for too long, cellulitis can upshot in pockets of pus (abscesses) or the spread of leaner into the bloodstream (bacteremia). However, most cases of cellulitis resolve with appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Who'southward at take chances?
Cellulitis can occur in anyone. Factors that increase the risk of developing cellulitis include:
- Diabetes
- Lymphedema
- Skin wounds
- Chronic lower leg swelling (edema)
- Athlete's human foot (tinea pedis)
- Bites from insects, animals, or other humans
- Obesity
- Poor apportionment in the legs (peripheral vascular disease)
- Weakened immune system due to underlying disease or medication
- Intravenous drug abuse
Signs and Symptoms
Cellulitis can bear on whatever part of the trunk, but the almost common locations are:
- Lower legs
- Artillery or hands
- Face
Cellulitis may be accompanied by swollen lymph nodes, fever, chills, and fatigue.
Self-Care Guidelines
If you think you take cellulitis, make an appointment to encounter your doctor. While you are waiting for the appointment with your physician, y'all can elevate the involved body part in guild to decrease swelling. A cool, make clean, moist towel can be practical to the surface area to decrease pain.
When to Seek Medical Care
If you develop a tender, red, warm, enlarging area on your skin, make an engagement with your physician as soon as possible to go treatment and to avoid complications that may occur if cellulitis is left untreated. If you also have fever and chills, or if the area involves the face up, you should go to the emergency room.
If y'all are currently being treated for a skin infection that has non improved after two–3 days of antibiotics, render to your doctor. You may need handling with unlike medications, or the infection may have spread deeper into your skin.
Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) is a strain of "staph" leaner that is resistant to antibiotics in the penicillin family. This form of antibiotics has been the cornerstone of antibody therapy for staph and skin infections for decades. CA-MRSA previously infected simply minor segments of the population, such as health care workers and persons using injection drugs. Still, CA-MRSA is now a mutual cause of skin infections in the general population. While CA-MRSA bacteria are resistant to penicillin and penicillin-related antibiotics, most CA-MRSA infections tin can easily be treated with commonly available nonpenicillin antibiotics. Rarely, CA-MRSA tin can cause a deeper skin infection, which usually requires intravenous (Four) antibiotics to treat the infection. At that place is an boosted strain of MRSA (hospital-acquired MRSA), ordinarily found in health care settings, that is susceptible only to intravenous antibiotics, so admission to the hospital is often needed for effective handling.
Treatments Your Physician May Prescribe
Your physician will usually be able to easily diagnose cellulitis by examining the affected surface area. Sometimes your doctor may want to go additional information by ordering blood tests and/or performing a bacterial culture in order to identify the specific bacterium that is causing the cellulitis as well every bit to test its susceptibility to different antibiotics to help guide treatment decisions.
A bacterial civilisation involves the following:
- Opening a blister or pus-filled crash-land with a needle, scalpel, or lancet after cleansing the peel.
- Rubbing a sterile cotton fiber-tipped applicator beyond the peel to collect the sample.
- Sending the specimen to a laboratory.
While waiting for the results from the bacterial culture, your medico may want to start you on an antibiotic to fight the most mutual bacteria that cause cellulitis. Once the final culture results accept returned, your physician may change the antibiotic you lot are taking, especially if the infection is not improving.
Mild cases of cellulitis in a healthy person can exist treated with oral antibiotic pills. Common antibiotics that are used to care for cellulitis include the following:
- Dicloxacillin
- Cephalexin
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- Clindamycin
- Doxycycline
- Linezolid
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
- Cefazolin
- Vancomycin
Trusted Links
MedlinePlus: CellulitisClinical Information and Differential Diagnosis of CellulitisReferences
AN, Swartz MN, Johnson RA. Soft-tissue infections: Erysipelas, Cellulitis, Gangrenous Cellulitis, and Myonecrosis. Wolff Thou, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller Equally, Leffell DJ, eds. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in Full general Medicine. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2008:1720-1731.
Bolognia, Jean Fifty., ed. Dermatology, pp.1123-1124. New York: Mosby, 2003.
Freedberg, Irwin M., ed. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. 6th ed, pp. 1845, 1848, 1883. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003.
Source: https://www.skinsight.com/skin-conditions/adult/cellulitis
Posted by: rodriquezfiesenioncid.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Long Does My Skin Leak After Cellulitis"
Post a Comment